

With this guide, you now understand how to handle the tar files easily.Are you a Linux user looking for a powerful tool to compress and extract files? Look no further! The tar command in Linux is your go-to solution. We covered the various options you have when you need to unpack the tar files. Working with tar files shouldn’t trouble you anymore. We successfully unpacked the tar files using various options. Similarly, as in the following image, you can extract specific folders from the tar file. $ tar -xf archive-file -wildcards ‘*.txt’ In case of many files with the same extension and you want to extract them all, you can use the - wildcards followed by the extension. For instance, to extract two files, file1 and file2, the command would be: $ tar -xfv file1 file2 If you don’t need to extract all the contents of the tar file, you can specify which specific files to extract by specifying their names separated by spaces. For this, use the -C flag followed by the path. You can extract the contents of a tar file to a different location instead of the default, which is the current directory. You must add the -f to specify which tar file to extract. For instance, to view the contents of our tar.gz file, the command would be: $ tar -tf To list the contents of a tar file before extracting it, use the -t flag.
#Unpack tar linux archive#
Note that the extract options are the same despite the extension of the tar archive file. The new command would be: $ tar -xvf linuxhint.tar To display the extraction progress, add the -v flag.
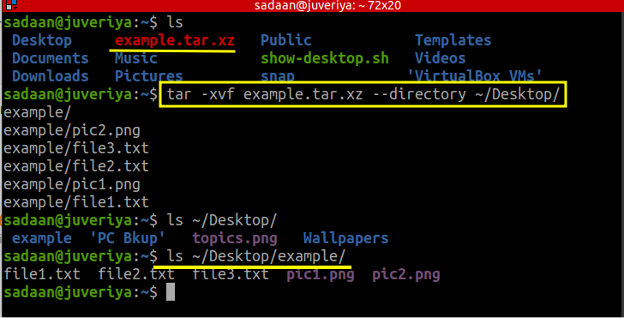
Replace the tar file with the one you are using for your case. The command would be: $ tar -xf linuxhint.tar To extract the tar file in the same directory, use the -xf flags followed by the tar file. Unlike GUI, the command line gives you more flexibility regarding what you can do when unpacking tar files. From there, you can extract the tar by clicking the extract button at the top-left corner. You can either choose Extract Here to extract the contents of the tar file in the current directory or use the Extract To and specify where you want to extract the tar files.Īlternatively, you can double-click the tar archive which lists the contents inside it. Next, right-click the tar file that you wish to extract. The first thing is to use your file manager and navigate to where the tar archive is located. To extract the tar files, use the Command Line or the GUI. With our two archive files, we can unpack them using tar. The syntax would be: $ tar -czvf file1 file2 file_n Next, let’s create a “.tar.gz” using the gzip compression.
To create an archive file, the syntax would be: $ tar -cf file1 file2 file_n We will see how to use them using the following examples:įor this example, we will create an archive file using tar and then cover the two ways of unpacking it. There are various options that you can use with tar. You can confirm by checking its version, as in the following image: Working with Tar Command in Linuxįor most Linux distributions, the tar command comes preinstalled. If you are looking on how to unpack the tar files, this guide covers how to create tar files and the two ways of unpacking tar files in Linux. Tar files support various compression such as gzip, which have the. Tar is meant for compressing magnetic tapes, and it stands for “ tape archive”. Besides, creating tar compressed files is easy using the programs like gzip. When using Linux, you are guaranteed to see tar files, especially when downloading the open-source packages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
